What is ReBAC?
ReBAC, or Relationship-Based Access Control, is an access control model where permissions to access certain resources are determined based on the relationships between the users and resources. Instead of relying solely on roles or attributes of users and resources, ReBAC considers the relationships between them.
Real-life ReBAC examples
Here are two real-life scenarios where Relationship-based access control would be implemented to enforce user actions.
Example #1: Social Media Platform
On Facebook, a user might set their photo album's privacy settings to be viewable only by "Friends of Friends." Here, access to the photo album is not just based on direct relationships ("Friends") but also an indirect relationship ("Friends of Friends").
Example #2: Collaborative Document Editing Platform
Alice and Bob are working on a project report in Google Docs. Alice creates the main document, and Bob adds supplementary material as an appendix in a separate document. Alice then links Bob's appendix to the main report. Now, anyone with permission to edit Alice's main report should also automatically gain permission to edit Bob's appendix because of the linkage (or relationship) between the two documents.
Check out this Google Drive example being modeled with Permit.
Basic definitions
Role Assignment
Role Assignment refers to the act of designating specific roles to individual users or entities, effectively granting them the permissions associated with those roles. Roles represent a collection of permissions. By assigning a user a particular role, you're essentially giving them access to all the permissions bundled within that role. This mechanism simplifies access management, especially in large systems or organizations, as administrators only need to manage roles rather than each specific permission for every user.
Example
In a company, new employees in the marketing department might be assigned the "Marketing" role, which provides access to relevant databases, software, and internal websites without having to configure each access permission individually.
Resource Role
A Resource Role is a specialized role that's specifically tied to a particular resource. This means that the role, and the permissions it carries, is relevant only in the context of that specific resource. By creating roles based on resources, organizations can have fine-grained control over who can access and modify specific items.
Example
In a cloud storage solution like Google Drive, a "Document Editor" role for a specific document might grant permissions to edit and comment on that document. However, having the "Document Editor" role for one document doesn't mean the user can edit all documents—only the specific one they're assigned to.
Role Derivation
Role Derivation is the process or mechanism by which new roles are formulated using existing roles as a foundation. This can be useful in hierarchical systems where higher-level roles encompass the permissions of several lower-level roles. Role derivation helps in creating roles that are a combination or subset of other roles, providing flexibility and ensuring that the principle of least privilege is maintained.
Example
In a software development company, there might be a basic "Developer" role that grants access to coding tools and repositories. A new "Lead Developer" role could be derived from the "Developer" role but with added permissions, like code review or project management tools. The "Lead Developer" role would, therefore, have all the permissions of the "Developer" role plus some additional ones.
Resource Relation
Resource Relations refer to the defined relationships or associations between different resources within a system. These relations are often used to model complex access control scenarios, especially in systems where access to one resource might be dependent on the relationship to another resource. By establishing these relationships, ReBAC can grant or deny access based on the context of both the user's attributes and the interconnected web of resources.
Example
In a healthcare system, a patient's medical record Resource A might have a treated by relationship with a specific doctor
Resource B. Only the doctors that have this "treated by" relation with a patient's record would have the permission to
access and modify it.
Resource Instance
Resource Instances refer to specific occurrences or representations of a resource in a system. While resource roles or types provide a generalized or abstracted idea of an entity, resource instances refer to a specific type of an entity. Understanding resource instances is crucial for systems that deal with a multitude of unique entities, each of which might have different access requirements.
Example
In a library management system, while Book might be a general resource type, each individual copy of a book, with its
unique ISBN or tracking number, is a Resource Instance. The instance Harry Potter and the Philosopher's Stone with
ISBN 978-0747532699 is different from Moby Dick with ISBN 978-1503280786.
Relationship Tuples
Relationship Tuples are structured sets that detail the relationships between resources and potentially users in the system. They represent the relationships between two specific instances of resources. Relationship tuples provide a clear, precise way to express and evaluate relationships in access control decisions.
Example
Using the healthcare system again, a Relationship Tuple might be represented as:
Patient John Smith Record treated by Doctor Jane Doe
This tuple indicates that Doctor Jane Doe has a treated by relationship with John Smith's medical record.
Whenever Jane tries to access the record, the system would evaluate such tuples to determine if she has the necessary
relationship-based permissions.
Modeling your system
As you begin to recognize the need for implementing ReBAC in your system, it might initially seem daunting to translate your application's elements into a coherent policy model. A helpful approach to gain clarity on your desired relationships is to create a visual representation.
Consider plotting out your resources as nodes and their interrelations as edges on a graph. This visual aid can greatly simplify the process and provide clearer insights into your access management.
Here is an example what a helpful mapping might look like:
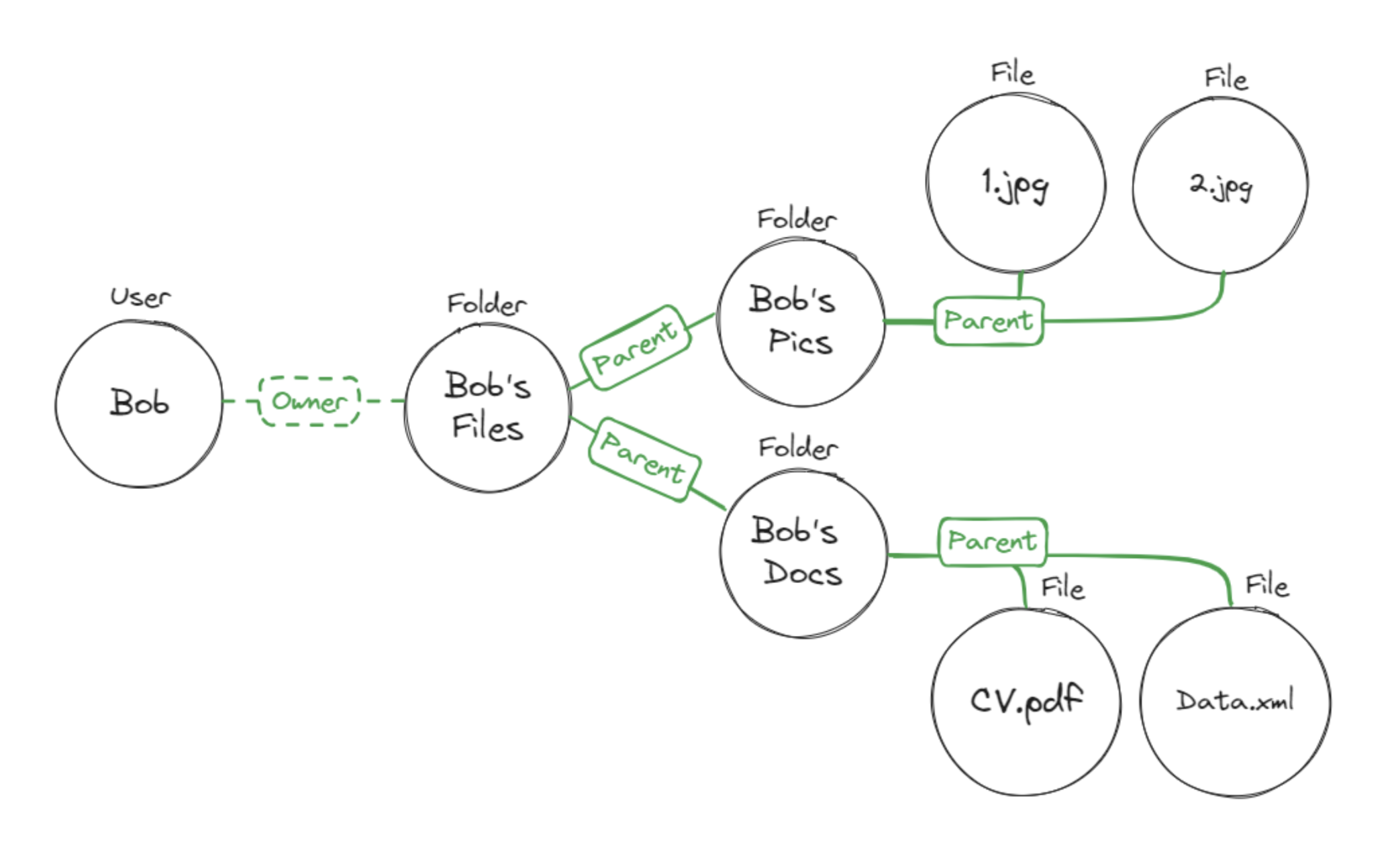
For a practical illustration of how the basic architecture should be segmented and represented in the Permit UI, please explore the following real-life example.